In 1916 Einstein wrote a book, “Relativity: The Special and General Theories”. In Chapter 5 he gave two specific measurements of the motion of the earth around the sun: aberration and Doppler shift. Below are the experiments Einstein was referring to.
Aberration
In 1725-1727 James Bradley discovered an unexpected shift in the position of stars that varied in direction throughout the year. It was determined that the shift was due to the earth’s velocity and direction in relation to the light. Specifically, the amount of the shift is equal to the ratio: (velocity of earth in orbit / (velocity of light). The amount of the shift is called the “constant of aberration”. James Bradley measured the aberration of many stars and came to a figure of 20.5 arc seconds for the constant of aberration. See Bradley’s 1727 paper listed below.
By 1910 the value for the constant of aberration was measured to be 20.4(45) arcseconds. See Encyclopaedia Britannica 10th edition linked below. The current measurement is 20.49551 arc seconds. The article on aberration in all Encyclopaedia Britannica editions back to 1771 is included below.
Stellar Aberration was initially published in 1727, Einstein was born in 1879, 152 years after it was first discovered. See the links to Encyclopaedia Britannica with articles on aberration starting with the first edition in 1771. Aberration was a well-known phenomenon long before Einstein was born.
External references to aberration:
- Analysis of Struve’s Constant of Aberration measurement
- https://explainingscience.org/2019/05/28/stellar-aberration/
- https://www.mathpages.com/rr/s2-05/2-05.htm
- https://www.usna.edu/Users/physics/mungan/_files/documents/Publications/TPT44.pdf
- https://www.chemeurope.com/en/encyclopedia/Aberration_of_light.html
Annual Doppler Shift
Hippolyte Fizeau, in 1848 measured red shift in stars.
William Huggins, in 1868 identified methods to view the Fraunhofer lines for different stars. WIlliam cataloged the lines for several stars: https://www.jstor.org/stable/108875
William Huggins, in 1871 first measured the velocity of a star moving away from the earth.
Vogel and Scheiner in 1887 measured the annual change in periodic change in the measured radial velocity of the stars due to earth’s rotation around the sun. This is specifically what Einstein was referring to.
A History of Astronomy, A. Pannekoek, page 451 https://www.astro.ru.nl/~fverbunt/iac2011/pannekoek61.pdf

Vogel and Schneier’s Publication circa 1892: https://www.google.com/books/edition/Publikationen_des_Astrophysikalischen_Ob/upNOAQAAMAAJ?hl=en
Direct PDF Download: Publikationen_des_Astrophysikalischen_Ob 1892
See also:
Henry Draper, 1872
Pickering, 1889
Stellar Parallax
In addition to Aberration and Red Shift, there are other measurements of the earth’s orbit around the sun.
In 1839 Friedrich Bessel measured the parallax of star 61 Cygni to be 0.314 arcseconds: https://doi.org/10.1002/asna.18390160502
Direct PDF Download: bessel1839
Several other early parallax measurements.
- On the Parallax of Alpha Centauri
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 4, Issue 19, January 1839, Pages 168–169
- https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/4.19.168
- Published: 11 January 1839
- On the Parallax of Sirius
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 5, Issue 2, November 1839, Pages 5–7
- https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/5.2.5
- Published: 08 November 1839
- A Letter from Professor Henderson to the Secretary, on the Parallaxes of certain Southern Stars
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 5, Issue 26, December 1842, Pages 223–225
- https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/5.26.223
- Published: 09 December 1842
- Parallaxes of 23 stars determined from plates taken with the McCormick 26-inch refractor
- Parallaxes of 44 stars determined from plates taken with the McCormick 67-cm refractor.
- Parallaxes of 31 stars determined from plates taken with the McCormick 26-in. refractor.
- Parallaxes of 20 stars determined from plates taken with the McCormick 26-in. refractor.
- Parallax and orbital motion of the astrometric binary BD +6° 398
Difference in Jupiter Moon’s Eclipse Time
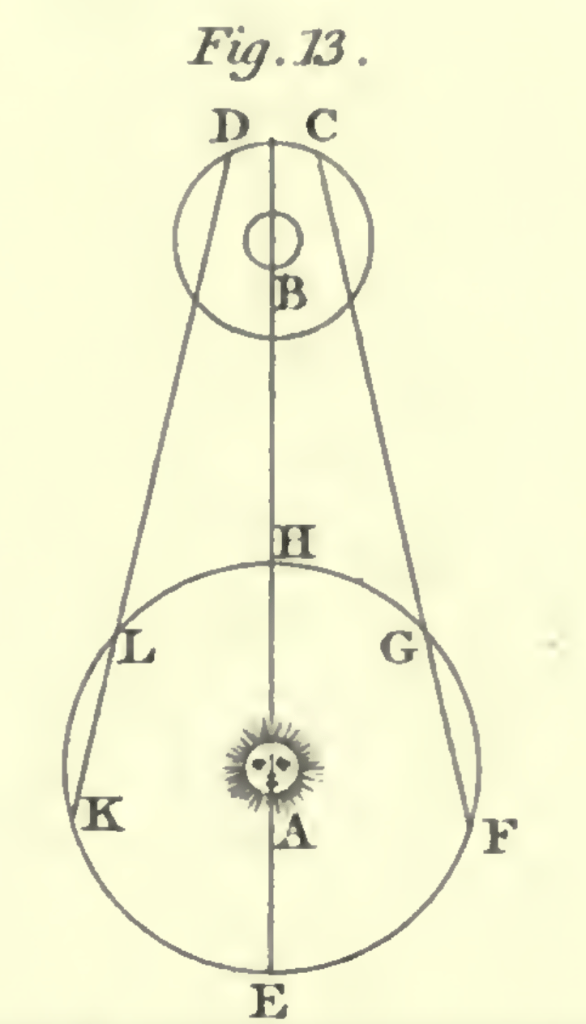
In 1676 Ole Rømer measured a difference in the time if took for Jupiter’s moon Io to pass into Jupiter’s shadow. This was determined to be due to the increased distance from Jupiter because of the location of earth in orbit around the sun.
In the diagram Jupiter is at position B, Io, Jupiter’s moon is orbiting and passes into Jupiter’s shadow between position C and D. The time that the passage is seen is several minutes later when earth is at position F than G or H.
The details written by Rømer were lost in a fire but historical accounts credit him with the initial discovery. The measurements have been repeated several times.
One of the historical accounts can be found in Philosophical Transactions or the Royal Society Vol II 1672-1683 Pages 397-398.
Here is a class assignment that asks students to find different measurements of the movement of the earth:
https://ecampus.matc.edu/mihalj/astronomy/discussion/unit2dogx/moving_earth_answer.htm